Standalone 5G architecture:
-
Context
- India’s largest telecom company Reliance Jio has announced the launch of its 5G services in Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai. The company said it will launch its 5G services on a “standalone” 5G architecture.
-
About 5G Network:
- There are three types of 5G spectrum bands: low-band, mid-band, and high-band. Each band is made up of a group of radio frequencies whose speed (performance) and reach (propagation) vary from one band to the next.
- It is important to understand that in the context of 5G spectrum bands, performance and propagation have an inverse relationship. Bands with high propagation have limited performance, and high-performing bands have limited propagation.
-
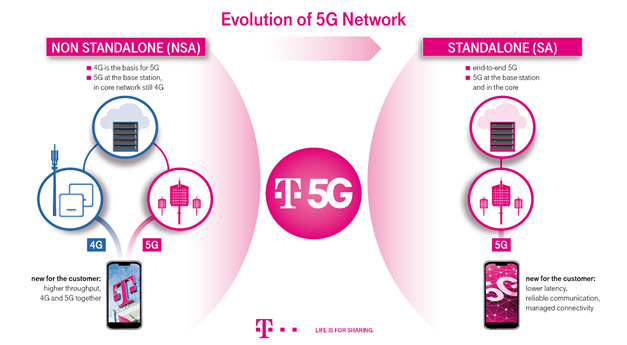
What are the two different modes of 5G networks?
- 5G networks are deployed mainly in two modes: Standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA).
- In practice, many operators have started their 5G rollout journey with an NSA deployment, and a view to graduation to a standalone deployment within a few years.
- SA deployment definitely offers an edge over the NSA, but it is cost intensive.
-
What is standalone 5G Architecture?
- SA 5G stands for Standalone 5G, means it’s an end-to-end 5G network. To understand how SA offers a complete 5G network, first, we need to know the intermediaries in a network. The intermediaries in a mobile network are:
- Base station (also called core)
- Radio antennas
- End device (smartphone, tablets, etc.)
- In an SA 5G network, the base station is entirely built on the 5G specification. The radio antennas are also based on 5G specifications. Lastly, the end devices must also support the 5G New Radio (NR) bands.
5G New Radio (NR) is the global standard for a unified, more capable 5G wireless air interface.
- In this ecosystem, all three pieces of equipment are purely based on the latest global 5G specifications. There are no 4G/LTE or existing legacy components used in this infrastructure. This kind of end-to-end 5G network is called Standalone 5G.
- Here, not just data but even voice calls (VoNR) will be done over 5G NR radios, offering a superior experience.
-
Key differentiators between standalone and non-standalone 5G networks:
- Standalone 5G uses the 5G New Radio (NR) access network which is a set of standards that replaces the LTE network 4G wireless communications standard.
- The standalone 5G architecture is based on an end-to-end core 5G network that is built from scratch.
- The equipment and network functions used in this model are built keeping 5G specifications in mind.
- The non-standalone 5G, on the other hand, offers a 5G radio signal using the existing 4G LTE core which means it is built over an existing 4G network while the standalone allows completely independent operation of a 5G service.
- The non-standalone 5G can be rolled out faster as it uses the existing 4G infrastructure, however, when it comes to stability and speed, the standalone 5G is better.
Standalone (SA)
Non-Standalone (NSA)
Pros
- Full 5G capabilities available
- New features, functionality, and services enabled (e.g., network slicing)
- More flexible architecture and dynamic linking of network functions
- Faster rollout – can act as a stepping stone as part of the transition to SA deployment
- Maximize utilization of existing network assets
- A lower level of investment required
Cons
- A higher level of investment required
- Organizational training required for 5G core and service operation
- Less flexible architecture
- Limited incremental 5G functionality
-
Key differences between 4G vs. 5G network Architecture:
- Latency: 5G promises low latency under 5 milliseconds, while 4G latency ranges from 60 ms to 98 ms. In addition, with lower latency comes advancements in other areas, such as faster download speeds.
- 5G standalone enables super-fast response times and faster access to higher data rates, which are required by Cloud gaming, immersive media, and vehicles or robot control.
- Potential download speeds: Internet speeds on 5G could touch 10 Gbps, compared to the 100 Mbps peak of 4G.
- Base Stations: Like its predecessors, 4G transmits signals from cell towers. However, 5G uses small cell technology, due to its faster speeds and mm-Wave frequency bands, so carriers will deploy high-band 5G in small cells about the size of pizza boxes in multiple locations.
- OFDM Encoding: OFDM (Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) is used to split different wireless signals into separate channels to avoid interference, which also provides greater bandwidth.
- Cell Density: Small cell technology enables 5G to provide more cell density and enhance network capacity. In 5G, networks will be denser, which means they have more capacity to support more users and connected devices, leading to increased mobile device and connection capacity.
- Network slicing: Network slicing will allow operators to create dedicated segments of the network to serve specific customers or use cases, with dedicated service level agreements (SLAs), policy control, and quality of service.
- Each network slice will present an opportunity for operators to monetize their network differently from the current mode of operation.
- 4G and earlier generations of cellular data services did not and could not support network slicing.
-
How is the 5G smartphone ecosystem in India shaped?
- The share of 5G smartphones in India has been on a steady rise over the last two years. As of now, the 5G-enabled smartphones accounted for a paltry 3 per cent of overall smartphone shipments in India, which is expected to grow to 35 per cent by the end of 2022.
-
Why is Reliance Jio betting big on standalone 5G architecture?
- With Stand-Alone 5G, Jio can deliver new and powerful services such as low latency connectivity, massive machine-to-machine communication, 5G voice, Edge computing and network slicing, and the
- A standalone 5G architecture offers a better mix of the spectrum, and carrier aggregation means that Jio standalone 5G will be able to offer a combination of coverage, capacity, quality, and affordability.
- As most telecom operators at present are deploying a version of 5G called non-standalone 5G, which is essentially a 5G radio signal delivered over an existing 4G infrastructure. It offers Reliance Jio over its rival service providers.

