How does tokenization prevent online card fraud?
-
Context
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated the tokenization of credit/debit cards for online merchants from October 1st, 2022.
-
What is tokenization?
- Tokenization refers to the process of replacement of actual card details with a unique alternate code known as the 'token', which shall be unique for a combination of card, token requestor, and identified device.
- A tokenized card transaction is considered safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant during transaction processing.
- Customers who do not have the tokenization facility, will have to key in their name, 16-digit card number, expiry date, and CVV each time they order something online.
- As of now, about 19.5 crore tokens have been created. Opting for Card-on-File Tokenization (CoFT) services, (creating tokens) is voluntary for cardholders.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has permitted authorized card payment networks to offer card tokenization services to consumers requesting it, in an effort to improve the safety and security of card transactions.
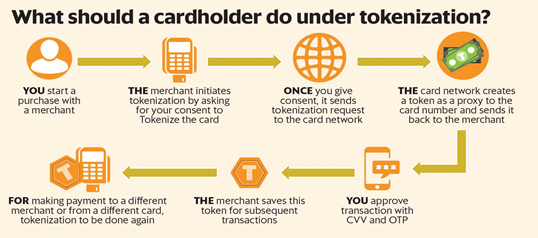
- Tokenization refers to the process of replacement of actual card details with a unique alternate code known as the 'token', which shall be unique for a combination of card, token requestor, and identified device.
-
What is the new guidelines say on functioning Of Online Transactions?
- From 1st October 2022, merchants will not be allowed to store your card numbers, CVV, and expiry date for processing online transactions unless the card number is tokenized.
- Any existing details that were saved by merchants will be deleted.
- To ensure ease of online payments, we encourage you to tokenize your Debit Card(s) and/or Credit Card(s) details at your preferred website/apps soon.
What is Card-on-File (CoF)?
- A CoF transaction is a transaction where a cardholder has authorized a merchant to store the cardholder’s Mastercard or Visa payment details.
- The cardholder then authorizes that same merchant to bill the cardholder’s stored Mastercard or Visa account.
- E-commerce companies and airlines and supermarket chains normally store card details in their system.
-
Why is the Tokenization of Cards Required?
- Many entities involved in an online card transaction chain store card data like card number and expiry date Card-on-File (CoF) for undertaking transactions in the future. While this practice does render convenience, the availability of card details with multiple entities increases the risk of card data being stolen or misused.
- There have been instances where such data stored by merchants have been compromised.
- Many jurisdictions do not mandate an Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA) for authenticating card transactions, stolen data in the hands of fraudsters may result in unauthorized transactions and resultant monetary loss to cardholders. Within India as well, social engineering techniques can be employed to perpetrate fraud using such data.
-
Why is tokenization necessary?
- Tokenization reduces risk from data breaches: Tokenization helps protect a business from the negative financial impacts of data theft. Even in the case of a breach, valuable personal data simply isn't there to steal.
- Tokenization helps foster trust with your customers: Consumers don't want their payment data falling into the wrong hands. Beyond avoiding the worst-case scenario of a data breach, using advanced security such as tokenization, fosters customer trust.
- Tokenization means less red tape for your business: Businesses that accept credit and debit cards need to be in compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Tokenization makes achieving and maintaining compliance with industry regulations significantly easier.
- Tokenization drives payment innovations: From the secure in-store point-of-sale acceptance to payments on the go, from traditional eCommerce to a new generation of in-app payments, tokenization makes paying with the devices easier and safer than ever.
-
What are the cases (instances/scenarios) for which tokenization have been allowed?
- Tokenization has been allowed through mobile phones and/or tablets for all use cases/channels (e.g., contactless card transactions, payments through QR codes, apps, etc.)
Three steps have to be completed for the smooth implementation of tokenization:
- Token provisioning: The consumer’s card number should be convertible into a token, which means the card networks have to be ready with the relevant infrastructure.
- Token processing: Consumers should be able to complete their transactions successfully through the tokens.
- Scale-up for multiple use cases: Consumers should be able to use the token for things like refunds, EMIs, recurring payments, offers, promotions, guest checkouts, etc.
-
What are the benefits of tokenization?
- Less sharing of Personal Data: Tokenized card transaction is safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant.
- Ensure Safe transactions: Even if a hacker/scammer were to get their hands on one’s token number, they would not be able to make indiscriminate use of it.
- Specific in task allotted: The token generated upon request for a specific merchant is unique to a specific card number and is usable only on that particular site or mobile app.
- Stick to Technology: The unique token generated for a specific site is only applicable on that site and nowhere else. The token is useless outside of that merchant’s ecosystem.
Implementation of the tokenization request:
- The tokenization request is then carried out through the Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA) by the cardholder.
- This algorithmically generated token protects sensitive information and prevents card fraud as it allows you to make payments without exposing your bank details.
-
Conclusion
This one of the Significant steps regarding the safety and transparency of online transactions. Altogether such initiatives must be promoted and must be supported at ground level.

