Lightning in India
Context
Seventeen people have been killed by lightning over the last two days in various parts of Bihar, Six deaths have been reported from Bhagalpur district, while three people were killed in Vaishali, and two each in Banka and Khagaria. Other deaths happened in Madhepura, Saharsa, Munger and Katihar.
What is lightning?
- Scientifically, lightning is a rapid and massive discharge of electricity in the atmosphere some of which is directed towards earth.
- Discharge of electricity: The discharges are generated in giant moisture-bearing clouds that are 10-12 km tall.
- Base of cloud: The base of these clouds typically lie within 1-2 km of the Earth’s surface, while the top is 12-13 km away.
- Temperature: Temperatures in the top of these clouds are in the range of –35° to –45°C.
- Moving up of water vapour: As water vapour moves upward in the cloud, the falling temperature causes it to
- Crystal formation: As they move to temperatures below 0°C, the water droplets change into small ice crystals.
- Heavy mass: They continue to move up, gathering mass until they are so heavy that they start to fall to Earth. This leads to a system in which, simultaneously, smaller ice crystals are moving up and bigger crystals are coming down.
- Release of electrons: Collisions follow and trigger the release of electrons, a process that is very similar to the generation of sparks of electricity.
- Chain reaction: As the moving free electrons cause more collisions and more electrons, a chain reaction ensues.
- Positive and negative charge: This process results in a situation in which the top layer of the cloud gets positively charged, while the middle layer is negatively charged.
- Flow of massive current: The electrical potential difference between the two layers is huge, of the order of a billion to 10 billion volts. In very little time, a massive current, of the order of 100,000 to a million amperes, starts to flow between the layers.
- Earth becomes positively charged: While the Earth is a good conductor of electricity, it is electrically neutral. However, in comparison to the middle layer of the cloud, it becomes positively charged. As a result, about 15%-20% of the current gets directed towards the Earth as well.
- It is this flow of current that results in damage to life and property on Earth.
- Direct lightning strikes are rare but even indirect strikes are fatal given the immense amount of charge involved.
Types of lightning
- In simple terms, lightning is a giant spark of electricity in the atmosphere between clouds, the air, or the ground. Broadly, there are three forms of lightning:
- Inter-cloud
- Intra-cloud
- Cloud-to-ground
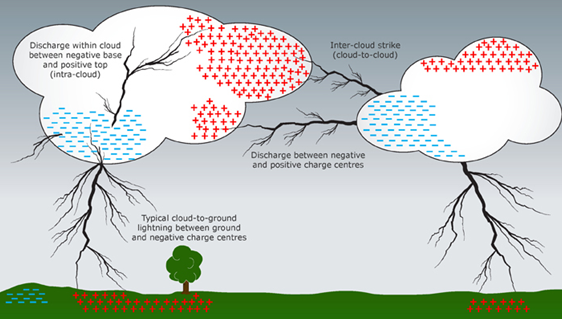
- It is the cloud-to-ground form of lightning that kills humans, as well as animals and livestock, and can substantially damage property.
- A typical lightning flash is about 300 million volts and about 30,000 amps.
- To put it in perspective, household current is 120 volts and 15 amps. A flash of lightning is enough to light a 100-watt incandescent bulb for about three months.

