The decade of Action: Importance of a circular economy
-
Background
- It is a multifaceted concept that came during the diverse schools of thought in the late 20thcentury and was widely adopted in the 21st
- Europe and China are leading some of the leading nations towards the adoption of a circular economy with many other international actors.
- The concept of circular economy has gained more traction after the launch of national circular roadmaps along with the emphasis by the EU Commission President by announcing it as one of the most important topics.
Some important take on circular economy
- In 2018, the World Economic Forum, World Resources Institute, Philips, Ellen MacArthur Foundation, United Nations Environment Programme, and with over 40 other partners launched the Platform for Accelerating the Circular Economy (PACE).
- In 2017, the British Standards Institution (BSI) developed and launched the first circular economy standard "BS 8001:2017 Framework for implementing the principles of the circular economy in organizations.
- The Netherlands government aims to reuse 50% of all materials as far as possible by 2030. It also aims to make the country shift towards a 100% waste-free economy by 2050.These objectives were setthrough a governmental circular economy, raw materials agreements, and transition agendasthat focus on the five most important sectors for waste: biomass and food, plastics, manufacturing industry, construction, and consumer goods.
- Germany is a leader in some aspects of the circular economy such as waste management and recycling.
- France has also launched the roadmap for circular economy in 2018 which consists of 50 measures for a successful transition to a circular economy.
- Belgium also scored second in the circular material use rate.
- Other notable countriesthat are working towards a circular economy are Italy, the United Kingdom, Austria, Slovenia, and Denmark.
-
Analysis
What isthe circular economy?
- A circular economy is an economic system, which is aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources.
- The Circular systems employ reuse, sharing, repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling to create a closed-loop system.
- This economy involves using waste materials and energy as input for other processes.
- It emphasizes minimizing the use of resource inputs and along with the lesser creation of waste, pollution, and carbon emissions.

- The circular economy aims to keep products, equipment, and infrastructurefor a longer duration and thus improving the productivity of these resources.
- This is a regenerative approach and is in contrast to the traditional linear economy.
- Liner economy has a "take, make dispose of" model of production.
Covid-19 and Circular economy
During the COVID-19 crisis, the significance of the circular economy has come to the forefront. The current crisis can have a positive impact on circularity in some of these ways:
- There is a need to rebalance the global economic system and in building a resilient economy that takes health and well-being as important variables of a future system.
- The COVID-19 crisis has demonstrated the vulnerability of global supply chains which makes us think locally.
- The inabilitynot to travel farther has made us connect to our local community and push for digitization.
The circular economy addresses the environmental pressures by acknowledging economic resilience imperatives and strengthening social foundations.
-
Key paradigms of circular economy
There are five key paradigms to understand and implement the circular economy to achieve a more fundamental impact:
- Circular Economy as a part of climate agenda: Despitethe announcement of net-zero emission targets by the US and China, the climate pledges, the Paris climate deal; the world is expected to see the rise above 2 degrees Celsius. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has warned that going beyond 1.5°C to 2°C would increase extreme weather events that would see devastating social, environmental, and economic consequences.
- The Circularity Gap Report 2021 has identified a set of circular strategies that can help in keeping the planet on a well below 2°C trajectories by cutting emissions. This could be achieved by reducing the volume of materials thatareused to create products and services, by using resources for a longer duration, and by replacing finite resources like fossil fuels with renewable energy resources.
- Circular economy as a “new, inclusive and green economy”:There is a need to find alternative solutions to resolve the contest between the environment and economy, while keep contributing to society. The linear economy is no longer fit for the purpose and an alternative is urgently needed.This makes room to show the viability of the circular economy on the ground.
- The circulareconomy is a global endeavor: The circular economy provides a new opportunity for providing a level playing field to build sustainable future economies. This will require better integration of social and human development considerations.The circular economy provides wellbeing for all within planetary boundaries.
- Circular economy towards Sustainable Development Goals: The circular economy is not a set of aspirational targets but it has process-oriented principles that create a positive impact. Practitioners of the circular economy should explicitly contribute to existing development frameworks including the Sustainable Development Goals.
India and the Circular Economy
- The significance of a circular economy for India raises to multifold by seeing its large population and its quest towards one of the biggest economies. At present most of the developed countries are making efforts towards the circular economy to which would be harmful to India to not restoring or regenerating its design of economy.
Some of the government initiatives
The government of India is actively formulating policies and promoting projects to drive the country towards a circular economy system. Two such critical areas are electricity from recyclable resources and waste management:
- The government is aggressively pursuing power generation through the abundant solar power through the creation of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and hasa target for generating 175 GW of energy by 2022.
- The governmentalso started the 'Swachha Bharat' initiative, at individuals, residential societies, commercial and educational institutions. Where the waste is getting segregated into green and dry waste. The green waste is converted into compost that enriches the soil and the dry or solid waste has the potential to reuse and recycle.
Benefits for India
- An estimated benefit for the circular economy path adopted by India could bring around 40 lakh crores or approximately US$ 624 billion in 2050.
- The greenhouse emission would reduce by 44% along with a significant reduction in congestion and pollution. Thus contributing to the health and economic benefits to the society.
- India produces approximately 1.40 lakh tonnes of municipal solid waste per day. It has the potential of generating an equivalent installed capacity of 200 MW.
- Circular Economy as a part of climate agenda: Despitethe announcement of net-zero emission targets by the US and China, the climate pledges, the Paris climate deal; the world is expected to see the rise above 2 degrees Celsius. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has warned that going beyond 1.5°C to 2°C would increase extreme weather events that would see devastating social, environmental, and economic consequences.
-
Future Potential of Circular Economy
Economic Benefits
- The concept of “circular economy” as a strategy for waste elimination has been broadly adopted in the business world. Companies have sought to achieve “zero waste” by finding uses for discarded materials and closing the loop in their supply network.
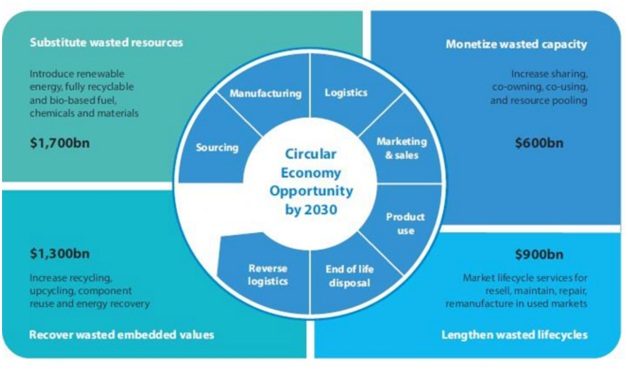
- Circularity offers economic benefits as well as reduces a company’s ecological footprint.
- It also improves business and community resilience by reducing dependence upon scarce resources and long-distance supply chains.
- The circular economy strategy would involve industrial and consumer waste replacement by virgin materials. It would remove inefficient and harmful waste disposal.
- The coal combustion residues from power plants, such as fly ash, bottom ash, boiler slag, and flue gas desulfurization residues, can be beneficially used in concrete and cement production, structural fills, building products, gypsum wallboard, and surface stabilization.
- The World Economic Forum estimated thatthe circular economy approach could save more than $1 trillion/year globally by the lower costs, lower carbon emissions, and supply chain risk reduction.
Environmental Benefits
- It enables the harmonization of industrial processes with natural processes that provide industries with important ecosystem services such as flood control, pollutant absorption, and carbon (C) sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems such as soil, vegetation, and wetlands.
- These services can mitigate climate change and air pollution, restore soil health, enhance the quality and renewability of water resources, and generally improve the environment.
- Best agriculture management practices such as conservation agriculture, integrated nutrient management, and sustainable intensificationcan increase soil resilience and restore the carbon pool, providing multiple benefits—greenhouse gas sequestration, improved water quality, and conservation decreased nutrient loss, reduced soil erosion, greater crop yields, and food and nutritional security.
Social Benefits
- The circular economy design also strives to be inclusive by considering the impact of management decisions on various stakeholder groups, including the poor and other underrepresented segments of society that are especially vulnerable to the health impacts of waste proliferation.
- The balance of natural capital and social capital (i.e., community solidarity) will help companies to achieve profitable waste reduction.
- Judicious management of all waste sources (industrial, agricultural and municipal) can advance progress toward many of the UN SDGs.
- The concept of “circular economy” as a strategy for waste elimination has been broadly adopted in the business world. Companies have sought to achieve “zero waste” by finding uses for discarded materials and closing the loop in their supply network.
-
Way Forward
The circular economy has huge potential in achieving sustainable goals and for reducing the impact of the economy on climate. In the present context of non-achievement of climate targets, this phenomenon can show the right path.

