Sixth Mass Extinction
Introduction
- More than 99% of all the living species that have ever existed on this planet are believed to be extinct.
- Extinction is a natural process and occurs at a constant rate.
- However, when the loss of species (i.e. extinction) exceeds the creation of new species (i.e. speciation), it is called as mass extinction.
- More specifically, loss of more than three-fourths of living species in a geologically short period of time is referred to as mass extinction.
- Our planet has been losing a huge number of species of flora and fauna since the previous two centuries.
- There has been a substantial increase in the degree of extinction. The ongoing extinction event is called sixth mass extinction.
- As humans are responsible for such a loss of living organisms. Therefore, sixth mass extinction is also called Anthropocene extinction.
- Furthermore, the extinction is occurring in the current Holocene epoch. Hence, the sixth mass extinction is also referred to as Holocene extinction.
- So far there have been 5 mass extinctions.
- These have occurred every 100 million years on an average, but their occurrence does not reveal any detectable pattern.
Previous mass extinctions
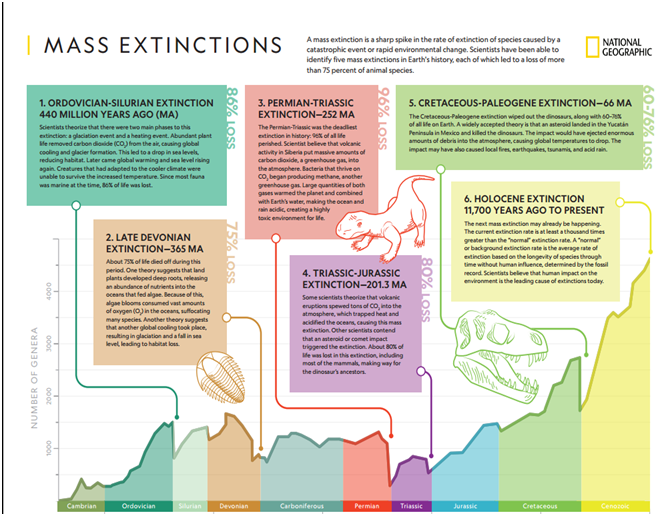
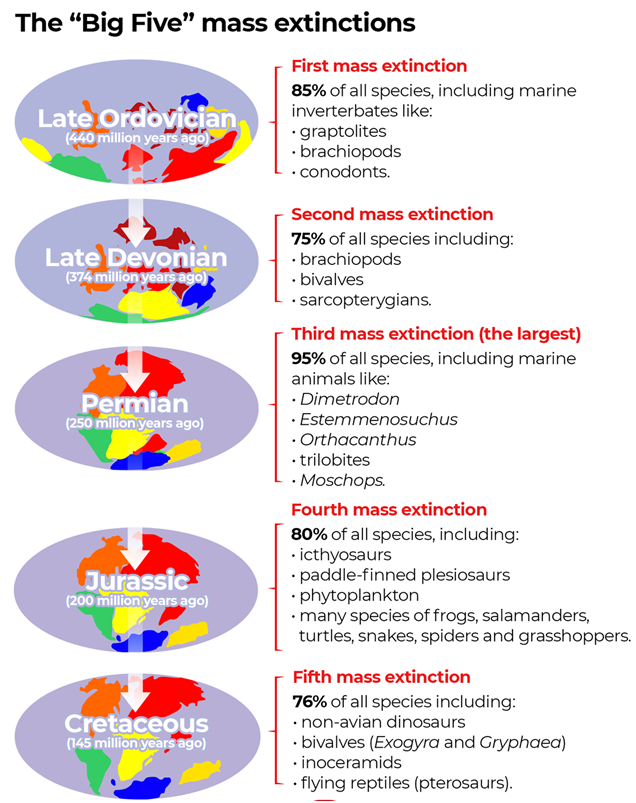
- First Mass Extinction
- It occurred at the end of Ordovician period around 440 million years ago.
- Nearly 86% of the living species were lost during the extinction event. Severe ice age decreased the sea levels, and exposed mountains such as the
- The newly exposed silicate rocks on these mountains sucked carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere, cooling the planet further.
- The event of huge glaciation was followed by a period of rapid warming. These changes were disastrous for the living organisms.
- Second Mass Extinction
- It occurred at the end of Devonian period around 383-359 million years ago. More than 75% of the species were lost.
- Emergence of terrestrial plants brought about growth of deep roots. These roots triggered weathering of rocks and released nutrients from land into the ocean. It could have triggered algal blooms which took away oxygen out of the water bodies. It must have suffocated the marine organisms such as the trilobites (bottom dwellers).
- Volcanism, accompanied by acid rain, asteroids, and emergence of invasive species could have also led to the extinction event, according to various hypotheses.
- Third Mass Extinction
- It occurred at the end of Permian period around 252 million years ago. Nearly 96% of the living species were lost during the extinction event.
- A majority of the insects and marine animals were wiped out. Siberian traps are the biggest cause of this extinction event.
- A large volcanic eruption released huge amount of lava, creating Siberia. This process emitted carbon dioxide into atmosphere. Further, methanogens released methane. These gases possess a strong global warming potential, which must have been responsible for the extinction event.
- Similar to second mass extinction, weathering could also be a trigger to the loss of living organisms by creating anoxic conditions.
- Fourth Mass Extinction
- It occurred at the end of Triassic period around 201 million years ago. Nearly 80% of the living species were lost during the extinction event.
- No clear reasons have been found out for the extinction event, but a rise in levels of greenhouse gases on an enormous scale triggered the extinction event.
- The rise in carbon dioxide could have acidified the oceans making it difficult for the marine organisms to produce calcareous shells, ultimately leading to their extinction.
- Fifth Mass Extinction
- It occurred at the end of Cretaceous period around 66 million years ago. Nearly 76% of the living species were lost during the extinction event. The non-avian dinosaurs were lost during this extinction event.
- A massive impact by an asteroid released huge amount of dust, and gases into the atmosphere. It resulted in excessive global cooling. The asteroid impact also led to a huge tsunami resulting in the extinction of living organisms. Volcanism has also been considered to be one of the reasons behind the extinction event.
-
- The reasons for the previous big five extinctions could be summarized as global cooling, global warming, extensive glaciation, sea level fluctuations, global anoxia, volcanic eruptions, asteroid impacts, plate tectonics, gamma rays, and disease outbreaks. These reasons have mostly worked in combination to be a causative factor for the extinction events.
Is sixth mass extinction a reality?
- The scientists have always debated the probability of sixth mass extinction being a reality.
- The critics argue that extinction of charismatic species could not be a reason to justify the extinction in present context as a mass extinction. However, they do believe that humans have caused enormous damage the planet and the living organisms thriving on it.
- More than 50% of living organisms that once shared the Earth with humans are already gone, and the next two decades would see more powerful assaults on biodiversity.
- It has been estimated that humans have caused extinction of around 1,000 species in the previous 200,000 years.
- Additionally, since 1500 we have been the reason for extinction of at least 322 animals. It includes species such as Passenger pigeon, Tasmanian tiger, Dodo, Quagga, Pyrenean Ibex, Sea Mink, Great Auk, Baiji, etc. More than 20,000 species are already threatened with extinction.
- Anthropogenic activities have resulted in a decrease in the population of any animal on the planet by 28% on average. Further, 33% of all the existing animal species are either in the threatened or endangered category.
The sixth mass extinction is bound to become a reality in the near future.
Reasons behind sixth mass extinction
The pace of the extinctions is a hundred times faster than they would have occurred naturally. If all the threatened species go extinct in the next century, and if the rate of extinction does not slow down, we might see mass extinction in the next 240 to 540 years.
Human beings have been the trigger to the occurrence of sixth mass extinction. Some of the major reasons responsible for the extinction of animal species are:
Over Hunting
- Various animals have been hunted for food, ornamental purposes and supposed medicinal effect, such as elephants for ivory, tigers for fur and organs, fishes for food and oil, shark’s fin for medicinal purposes, etc.
- Overfishing has been another major factor behind species loss.
Habitat Loss and Destruction
- Deforestation, and the resulting desertification, have devastated the habitat of a majority of the animal species. Tropical rainforests could disappear in the next 100 years if deforestation is not reversed.
- 13 million hectares of forest have already been destroyed or converted for other purposes.Apart from terrestrial degradation of forests, coral reefs have also been damaged extensively.
- Nearly 30% of the coral reefs have already been destroyed. The coral reefs provide habitat to one-fourth of the marine animals. Damaging these reefs would be disastrous for the species dependent on them.
Pollution
- The pollutants have damaged the ecosystems. Correspondingly, the pollutants, introduced into air, soil and water bodies, interfere with animal metabolism, rendering them liable to damage and death.
Invasive species
- They are the major cause behind species extinction in island ecosystems. Introduction of invasive species have led to extinction of several species which exists as native species in a particular area.
- Some of the species extinct due to invasive species are Yunnan lake newt (due to exotic fish and frogs in China in 1979), Hawaiian thrush (due to invasive predators), and Guam broadbill(due to brown tree snake).
Climate change
- The release of greenhouse gases has resulted in global warming and climate change. The consequences of climate change include habitat loss, shift in climatic condition, and altered competitive relationships.
- Climate change has also brought about changes in seasons, species range alterations, and differential seasonal breeding.
- It has been estimated that the rate of release of greenhouse gases by humans have exceeded the release rate of greenhouse gases by the Siberian Traps(which eventually triggered Third mass extinction).
- Climate change is also bringing about changes in sea level, which could have negative impact on coastal species
Impact of Extinction
- The extinction of living organisms could have multiple long-lasting impacts on the planet. These could be stated as follows:
Decrease in predator species
- Reduction in the number of large predators (such as cougars) would increase the population of herbivores (such as deer). Herbivores would consume more vegetation, which would alter the path of local streams, trigger desertification, and ultimately lower overall biodiversity.
- Interestingly, loss of predators such as lions and leopards, have boosted baboon population in Africa which are responsible for transferring intestinal parasites to humans living nearby.
- The loss of big predators has also driven many of the pandemics, population collapses and ecosystem shifts, the Earth has seen in recent centuries.
Collapse of food chain and food web
- Plants and animals depend on each other and on microbes, land, water, and climate to keep the entire ecosystem healthy and alive. Removal of one species would a trigger a series of changes that wouldn’t be easy to fix.
- In the words, alterations in species richness and evenness would be disastrous for the biodiversity.The ultimate outcome could be the collapse of food chain and food web, thereby threatening the existence of life on the planet.
Decrease in insect population
- Insects play a critical role in transferring pollen grains thereby accomplishing pollination in plants. Pollination is the key for survival and sustenance of the plant species.
- Decrease in insect population would also affect seed distribution, thereby affecting the biodiversity.
- Decrease in insect population would also damage the food chain and food web.
Deteriorating water quality
- Decrease in the population of suspension feeders, submerged vegetation and wetlands would decrease the filtering and detoxification services brought about by them. This would increase the risk of occurrence of harmful algal blooms such as red tide, thereby accentuating oxygen depletion from the water bodies and a deteriorationof water quality.
- Additionally, it would be disastrous for the aquatic organisms.
Loss of nature’s therapeutic riches
- A majority of the prescription medications contain chemicals obtained from plants or animals. Loss of such species could damage the health systems prevailing across the planet, thereby making human beings more vulnerable to diseases and the resulting deaths.
Economic impact
- A large decrease could be seen in terms of livelihoods of several human beings.
- Over-exploitation of various resources has resulted in their depletion, which would definitely be disastrous for the planet in the long-run.
- Overfishing has negatively affected the local fishermen and their livelihoods. A United Nations study reports that the extinction of species would diminish global economic output by 18% by 2050.
- A number of industries have already been impacted economically, such as decrease in bee populations has hurt global honey industry.
Will humans be victims of their own mass extinction?
- Previous extinctions have seen an increase in carbon content over a very short span of time. In the present context, carbon and other greenhouse gases are already increasing at a very rapid pace.
- Acceleration in carbon content by anthropogenic activities would make sixth mass extinction might become a reality by 2100 (The prediction is supported by a paper published by a geophysicist Daniel Rothman). The end could be much swifter if countries like the United States, North Korea, and China begin a nuclear war.
- The big question is will the human species be able to escape the mass extinction event? The third mass extinction removed96% of living organisms from the planet. Therefore, the probability that humans will survive the catastrophe is very small.
- The other big question is after our demise will we reappear on Earth? Taking evolutionary forces into account, there is no guarantee that we might return on this planet. If we do not undo the damage we have done, we may need to start searching for an alternative planet with a possibility of life.
Surviving mass extinction
- Having discussed the various extinction events, the reasons behind them, and the impact that the extinction could have on the planet, it also becomes important to look forward to ways to heal and, if possible, reverse the damage done. The possible suggestions are:
Biodiversity Conservation
- In-situ Conservation (national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves) and Ex-situ Conservation (zoos, nurseries, botanical gardens, gene banks, etc.) are important strategies to conserve biodiversity.
Legal Steps
- Most countries have environmental regulations but very few actually abide by them. A new U.N. report finds that to address climate change, we don't need new laws or regulations, but to get countries to comply with laws that already exist.
- Some of the laws existing in India to conserve the flora and fauna of India are:
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980
- The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- The Indian Forest Act, 1927
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- National Green Tribunal Act, 2010
- Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991, etc.
Constitutional Steps
- Under Part IVA of the Constitution (Article 51A- Fundamental Duties), the Constitution casts a duty on every citizen to improve and protect the nature and have compassion for all living beings.
- Further, the Constitution under Part IV (Article 48A- Directive Principles of State Policies) stipulates that the State shall try to improve and protect the environment and safeguard forests and wildlife of the country.
Individual Steps
- Refuse, reduce, reuse, and recycle for waste management; Refuse plastic products; Reduce personal carbon footprint; Adopt sustainable technologies; Prevent pollution of air, water, and soil resources; Save natural resources from getting exploited; Prevent spread of invasive and exotic species, etc.
Bringing back the dead to life
- Gene-editing technologies are being harnessed by the scientists to make animals produce offspring with DNA extracted from the extinct animals. For example, Crispr-Cas9 technology is being utilized by the scientists to revive the extinct passenger pigeon.
- If the initiative is successful, these birds would be the first animals brought back to life with traits from a species that no longer exists.
Conclusion
- It has been well established that anthropogenic activities have pulled the trigger of the gun loaded with massive extinction of living organisms. The sixth massive extinction is predicted to hit us by 2100.
- We must take adequate steps to conserve the existing biodiversity and prevent the living organisms from extinction, if we need to escape and survive the ongoing holocaust.
- The father of biodiversity Edward Osborne Wilson has rightly said “We should preserve every scrap of biodiversity as priceless while we learn to use it and come to understand what it means to humanity.”