Relevance of Mahatma Gandhi’s principles dealing pandemic
-
Context
The current COVID-19 Crisis, created by ‘western socio-economic model’, which is based on profits & consumerism, has revived the relevance of ‘Gandhian philosophy’ in today’s world.
-
Background
- The current pandemic is a wake-up call for the postmodern world, and it spotlights the relevance of Mahatma Gandhi’s principles loud and clear and to extract ourselves from the mesmerisation of modernity.
- Gandhi went as far as to discredit modernity’s alleged civilizational status as a “disease”.
- However, 21st century is the era of globalization, that moves on to make the world a global village.
- Nowadays, there is this belief that all emergent problems (ecological, social, economic, political and moral) could be resolved by technological innovations and further discoveries.
- Gandhi almost predicted the current pattern in the modern society in Hind Swaraj as he prepared its manuscript in 1908 in which he put forward four main goals. These are-
- Swaraj
- Non-violence
- Swadeshi
- Sarvodaya
-
Analysis
What is Gandhian ideology?
Gandhian ideology can be understood as the set of ideas based on religious and social concepts adopted and developed during Gandhi’s period in South Africa (1893 to 1914), and later in India.
- The philosophy is not only simultaneously political, moral and religious; it is also traditional and modern, simple and complex.
- Though, it embodies various Western influences to which Gandhiji was exposed, it was rooted in ancient Indian culture harnessing universal moral & religious principles.
- His ideology focuses not only on idealism, but on practical idealism. And it exists on several planes – such as the moral, political, economic, social, religious, individual and collective.
- The philosophy is a double-edged weapon, whose objective is to transform the society and individual simultaneously, in accordance with the principles of ‘truth’ and ‘non-violence’.
Mahatma Gandhi’s principles and its relevance to health
Gandhi once said, “It is health that is real wealth and not pieces of gold and silver.” Today, when everyone is running to acquire wealth while neglecting their health, there could not be any ‘better eye-opener’ than this quote.
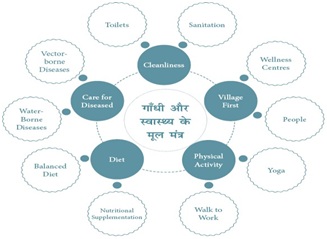
Important Gandhian principles which still hold true
1. Swadeshi - Applied meaning of swadeshi in multiple ways.
- Political dimension: The concept of Swadeshi is essential for the revival of the indigenous institutions and strengthening them.
- In 1909, Gandhi pleaded the need for internal governance (swaraj) in book Hind Swaraj or Indian Home Rule.
- He wanted to empower the people through political self-governance.
- His vision of decentralized political system was Panchayati Raj
- Religious dimension: Swadeshi guides to measure our glorious past and further enact it in the present generation.
- Economic dimension: Gandhi thought that the deep poverty prevailing among masses was resultant of the departure from the path of Swadeshi in the economic and industrial life.
- Gandhi advocated the use of product that are produced by our immediate neighbours and serve those industries by making them efficient, and strengthen them in areas where they are found deficient.
- Encouraging and reviving the indigenous industries.
- g: khadi was found as the most important corollary of the principle of Swadeshi
- Also, the recent ‘Make in India’ campaign is a re-imagined and modified version of the swadeshi movement.
- Gandhi's concept of Gram Swaraj can be very well appreciated in the light of the COVID pandemic.
Relevance
Global dependence on China has made this pandemic & its recovery difficult for Nations therefore need of hour.
2. Swacchata - “Sanitation is more important than independence”.
- Cleanliness and sanitation were made an integral part of the Gandhian way of living.
Relevance
- Gandhi practised and promoted personal hygiene and community sanitation, which has been advocated as Social Vaccine during this pandemic.
- Keeping surroundings clean helps in preventing most infectious diseases from contaminated water, oral faecal route etc.
3. Sarvodaya - Sarvodaya is a term meaning ‘Universal Uplift’ or ‘Progress of All’.
- The term ‘Sarvodaya’ was first coined by Gandhi as the title of his 1908 translation of John Ruskin’s tract on political economy, “Unto This Last”.
- It can be summed up as follows:-
- An individual’s good is contained in the ‘good of all’.
- A lawyer’s work has the same value as the barber’s in as much as all have the same right of earning their livelihood from their work.
- The life of the tiller of the soil and the handicraftsman is the real life worth living.
Relevance
Adhering to this principle would have mitigated the troubles faced by migrants & poor during the lockdown.
- This principle lays great emphasis on moral and spiritual values and it seeks to create new social and economic values.
- People will work for the good of all and family feeling will animate the entire community.
- Fullest scope for freedom, fellowship and equality.
- Shifting of world’s perspective from commerce driven economy to humanity driven economy.
4. Sustainable Living
- Mahatma Gandhi advocated living in harmony with environment, and eradicating exploitative practices as much as possible.
5. Emphasis on Ethics
- Gandhi called for integrating economics, politics and technology with ethics.
- If China was prompt about the initial outbreak of disease in Nov 2019, much of the damage could have been avoided.
Conclusion
In view of the catastrophic disruption caused in the global economy, now is the right time to rethink the Gandhian Principles of swachhta for protection from pandemic, swadeshi for self-reliance and self-sufficiency and finally Sarvodaya for betterment of lives. Moreover it would be the ideal moment to focus on regenerating our rural economy to bring about Gandhi’s cherished dream of gram swaraj.

