Punjab’s villages expands forest with Miyawaki method
Context
Kuharianwali, a village in the Fazilka district of Punjab, has become a trendsetter in expanding forest cover by applying the so-called Miyawaki method.
- As of 2021, according to data from the Forest Research Institute, the district had just 1.34 percent forest cover, one of the lowest in the state.
About Miyawaki method
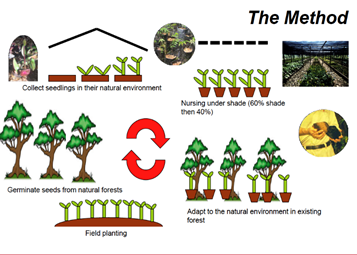
- Miyawaki is a technique pioneered by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, that helps build dense, native forests in a short time.
- It has revolutionised the concept of urban afforestation by turning backyards into mini-forests.
- This method includes planting trees (only native species) as close as possible in the same area which not only saves space, but the planted saplings also support each other in growth and block sunlight reaching the ground, thereby preventing the growth of weeds.
- The saplings become maintenance-free (self-sustainable) after the first three years.
Miyawaki Process
- The native trees of the region are identified and divided into four layers — shrub, sub-tree, tree, and canopy.
- The quality of soil is analysed and biomass which would help enhance the perforation capacity, water retention capacity, and nutrients in it, is mixed with it.
- A mound is built with the soil and the seeds are planted at a very high density — three to five sapling per square meter.
- The ground is covered with a thick layer of mulch.
Benefits of Miyawaki Method
- Faster Process and Dense Forest
- Faster Regeneration of Land
- Self-Sustainable Saplings
- Environmental Benefits

