Emission-Trading Markets
Context
India’s first experience with ETS was a pilot scheme for particulate matter (PM), introduced in 2019 in Surat, Gujarat.
-
Incidentally, this was the first time an ETS had been introduced for PM in the world.
What is an emission trading scheme?
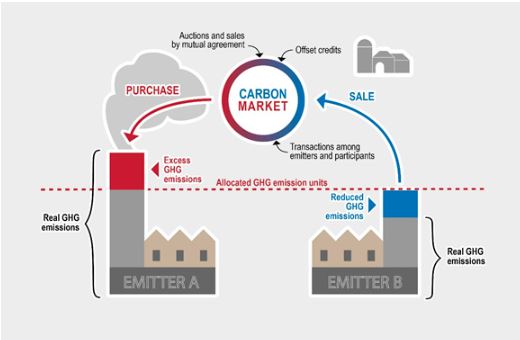
- Emission trading systems(ETS) is also referred to as the cap-and-trade system.
- Under ETS, the government caps the total level of greenhouse gas emissions provided to the companies and allows those industries with low emissions to sell their extra allowances to larger emitters.
- The programme aims to reduce particulate air pollution and facilitate robust economic growth.
- Under the programme,the government sets a cap on emissions and allows industries to buy and sell permits to stay below the cap.
- The Gujarat state pollution control board (GPCB) will define the total mass of pollution that can be released into the air over a certain fixed period by all industrial units together.
- This will be equivalent to the cap.
- The programme is the first market-based approach to regulate pollution emissions in India.
- Further,it is also the first in the world to regulate particulate air pollution.
- At present,the programme is being launched in Surat to understand its impact on emissions, industry costs and regulatory costs.
What is Particulate matter?
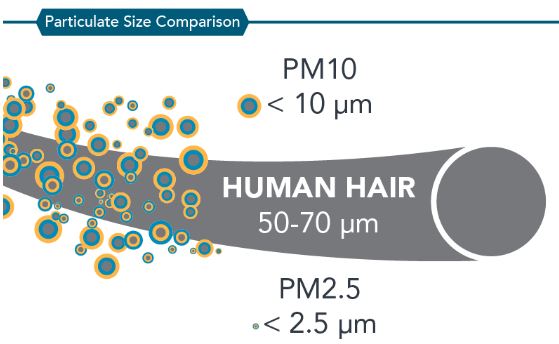
- Particulate Matter (PM) is small liquid droplets and solid particles whose hazardous nature increases with a decrease in their size as they become respirable.
- It includes both organic and inorganic particles, such as dust, pollen, soot, smoke, and liquid droplets.
Why was Surat chosen for the scheme?
- In the last five years, the quality of air in Surat has deteriorated.
- According to GPCB annual reports, pollution levels have increased between 120-220% in 2018.
- Surat was chosen because,
- Its industrial associations agreed to run the pilot scheme.
- They had already installed Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems, so that the mass of PM being released can be estimated.