‘BIMSTEC finalizes major connectivity master plan for Bay of Bengal region’
-
Context
Recently the 17th BIMSTEC Ministerial Meetingof the Foreign ministers of the Bay of Bengal Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) groupfinalized an aspiring air, land-linkages, and sea connectivity master plan that is expected to be adopted at its 5thsummit which isgoing to be hosted by Sri Lanka.
-
Background
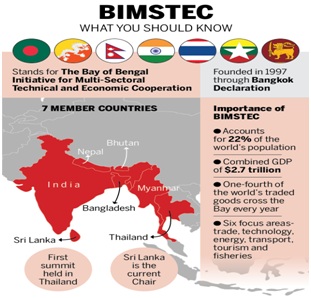
- BIMSTEC constitutes seven Member States:
- The five countries are from South Asia,including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka
- Twoare from Southeast Asia, that includes Myanmar and Thailand
- It came into existence in 1997 through the “Bangkok Declaration”.
- Initially, it had four Member States with the acronym ‘BIST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Sri-Lanka, and Thailand - Economic Cooperation).
- It was renamed as ‘BIMST-EC’ inBIMSTEC Transport Infrastructure and Logistic Study (BTILS) project in 2007.
- BIMSTEC connects the littoral countries of the Bay of Bengal and the Himalayan ecologies.
- It has emerged as a major instrument for regional cooperation with its primary focus on economic and technical cooperation among the countries of South Asia and south-east Asia.
- Its stability lies in that it includes two influential powers India and Thailand which lays-off fear the dominance by one big power.
- The grouping promotes increased connectivity with ASEAN countries and supports smaller countries like Bangladesh Bhutan and Nepal to develop connectivity with ASEAN nations.
- Transport and Communication is one of the 14 priority sectors of cooperation of BIMSTEC, since 1997. This sector is led by India.
BIMSTEC Priority Sectors:
SECTORS
LEAD COUNTRIES
1. Trade & Investment
Bangladesh
2. Technology/Sub-sector
Sri Lanka
3. Energy
Myanmar
4. Transportation & Communication
India
5. Tourism/Sub-sector
India
6. Fisheries/Sub-sector
Thailand
7. Agriculture/Sub-sector
Myanmar
8. Cultural Cooperation
Bhutan
9. Environment and Disaster Management
India
10. Public Health/Sub-sector
Thailand
11. People-to-People Contact
Thailand
12. Poverty Alleviation/Sub-sector
Nepal
13. Counter-Terrorism and Transnational Crime
India
14. Climate Change
Bangladesh
- BIMSTEC constitutes seven Member States:
-
Analysis
What is BIMSTECMaster Plan for Transport Connectivity?
- The Master Plan for BIMSTEC Connectivity has taken Trade intensity and the transportation linkages as the two determinants of regional integration.
- The connectivity master plancame as a result of consultation of more than a decade among the member states.
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB)also conducted study in 2007 and 2014, which identified 166 connectivity projects at an estimated cost of USD 50 billion. Out of these projects,65 projects were identified as priority projects.
- The plans talk about the Transportation and Cross-border Facilitation, Multimodal Transport, and Logistics support to create air, water, and land linkages among the Member States.
-
Arterial hyperlinks
The major arterial hyperlinks included within the master plan are:
- India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral freeway
- Kolkata-Birgunj and Kolkata-Kathmandu hyperlinks
- Kolkata-Siliguri-Guwahati-Imphal hyperlink
- Kandy-Colombo hyperlink
BIMSTEC Transport Infrastructure and Logistic Study (BTILS)
- BIMSTEC Transport Infrastructure and Logistic Study (BTILS) project was commissioned in 2007.
- It was funded by ADB.
- BTILS submitted the Report in December 2009.
- The purpose of the BTILS are given as:
- To make a profile for the transports and logistics of the region
- To identify the hard and soft infrastructure projects which are related to connectivity and trade
- To recommend future BIMSTEC policies and strategies for enhancing the connectivity and trade
- To recommend an effective institutional mechanism for monitoring and facilitation of implementing the priority projects.
-
Guidelines for the Implementation
- The Master Plan should be in compatibility of the ASEAN Connectivity 2025 Master Plan, but it has to be different.
- It should emphasize on the BIMSTEC’s bridge connectivity plan between South and South East Asia, ASEAN, and SAARC.
- Bilateral and trilateral joint Developmental Strategies are to be considered for the implementation of the plan For example,Trilateral Highway linking India, Myanmar and Thailand, Kaladan Multi-Modal Transport project.
Asian Development Bank
- ADB is committed to achieve a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific. It is also committed to support its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty.
- The number of ADB members has increased from 31, in 1966, to 68 members. The 49 members are from the Asia and the Pacific; and rest from outside this region.
- Its main instruments for helping its developing member countries are policy dialogue, loans, equity investments, guarantees, grants, and technical assistance.
-
BIMSTEC Motor Vehicle Agreement:
- BIMSTEC agreed for the BIMSTEC Motor Vehicle Agreementduring the Goa Retreat in October 2016.
- A Master Plan for BIMSTEC connectivity and BIMSTEC Coastal Shipping Agreement were also agreed to be carved out.
- Substantial progress is made in economic connectivity in terms of taking steps for energizing BIMSTEC integration, such as the BIMSTEC charter, energy grid interconnectivity, completion of the Master Plan for Transport Connectivity
- BIMSTEC countries are currently negotiating the
- BIMSTEC Coastal Shipping Agreement
- BIMSTEC Motor Vehicle Agreement
- Through this movethe traffic and trade will become easier between the countries India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, and Sri Lanka.
- All vehicles from BIMSTEC nations will require one permit to cross the border of any BIMSTEC member country.
- The BIMSTEC Motor Vehicle Agreement (MVA) will add huge impact on BIMSTEC's economic connectivity.
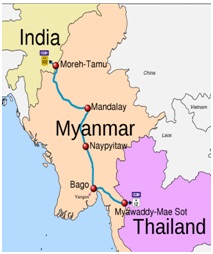
India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral freeway
- This involves India, Myanmar, and Thailand, and East-West Corridor.
- The project was conceived in 2002.
- It is a 1360 km transnational highway which connects the Moreh in India, Bagan in Myanmar, and Mae Sot in Thailand.
- The project could also look at extending the highway through other countries such as Cambodia, Vietnam, and Laos.
- The idea behind the project is to connect India up to the East Coast of Vietnam along with boosting connectivity within the BIMSTEC region.
-
What is the significance of the “BIMSTECMaster Plan for Transport Connectivity”?
- The projectcan play a significant role in accelerating the pace of economic development for the BIMSTEC region through the facilitation of trade and investment, tourism promotion, and people-to-people contact.
- The plan may enhanceseamless movement of goods and people, will improve transport interconnectivity, and will promote cultural exchange to benefit all parties involved.
- It talks about inland waterways connectivity that will give Nepal and Bhutan easy access towards the Bay of Bengal.
- The plan has potential for improving connectivity within the BIMSTEC region and inconnecting India to the east coast of Vietnam.
-
Conclusion
Robust connectivity is essentially required for economic integration of the region with smooth cross-border movement of people and goods.A combined effort is required for making seamless multi-mode transport hyperlinks and simplified transit services.The BIMSTEC master plan also seeks to promote synergy with other connectivity frameworks such as the “ASEAN master plan onconnectivity 2025”.The master plan is also a step towards fulfilling the people’s aspirations for better connectivity and integration in the region.

