55th anniversary of ASEAN
Context
Recently, ASEAN marked an important occasion of the 55th anniversary of ASEAN (the Association of Southeast Asian Nations).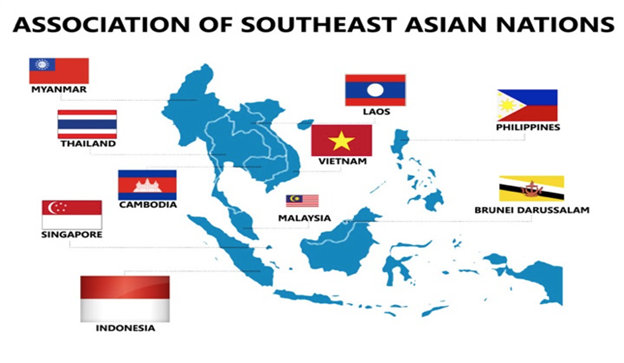
About Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- It is a political and economic organization aimed primarily at promoting economic growth and regional stability among its members.
- It was founded in 1967 by the five South-East Asian nations of Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam joined in 1984, Vietnam in 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999, making up ten Member States of ASEAN.
Current members
- Current members: ASEAN include Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam.
- ASEAN Plus Three: It is a forum that functions as a coordinator of co-operation between the ASEAN and the three East Asian nations of China, South Korea, and Japan.
- ASEAN Plus Six: The group includes ASEAN Plus Three as well as India, Australia, and New Zealand.
About ASEAN Summit
- It is the highest policy-making body in ASEAN comprising the Head of States or Government of ASEAN Member States.
- Summit is held twice annually.
- The First ASEAN Summit was held in Bali, Indonesia in 1976.
ASEAN - India Relations
- Multi-level interaction: Engagement with ASEAN is a multi-level interaction process.
- At the apex is the annual summit “ASEAN-India Summit”.
- Summits are supported by meetings at the Foreign Minister level “ASEAN-India Foreign Ministers Meeting”-AIFMM.
- India shares a deep connection with ASEAN and has continued its active engagement in many areas contributing to regional peace and stability, particularly through ASEAN-led mechanisms, such as:
- East Asia Summit.
- ASEAN Regional Forum.
- ADMM-Plus.
- The ADMM Plus is an annual meeting of Defence Ministers of 10 ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) countries and eight dialogue partner countries - Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia and the United States.
- Delhi Dialogue: The ‘Delhi Dialogue’ (DD) mechanism hosted by India annually.
- It is traditionally inaugurated jointly by India and ASEAN at the Foreign Minister’s level.
- It serves as the main Track 1.5mechanism for our engagement.
- The DD-mechanism allows the participation of think tanks, academics and prominent civil society persons from both India and the ASEAN region.
- In addition to government representatives, with the objective of contributing ideas and perspectives to furthering the India-ASEAN strategic partnership.
- The XIIth edition of the Delhi Dialogue was held in June, 2022.
- Act East Policy & Indo-Pacific: Indo-Pacific is an interconnected geography where ASEAN is at its core.
- Both ASEAN and India believe that openness, inclusiveness, rules-based order, freedom of navigation and peaceful settlement of disputes lie at the very core of the Indo-Pacific.
- Maritime Connectivity & Security: India is surrounded by the Indian Ocean and ASEAN Countries have borders with Indo-Pacific waters.
- This opens up plenty of opportunities for India and other countries to work on maritime security, trade, and better supply chain networks.
- India is consciously working with ASEAN towards a vision of an open and inclusive Indo-Pacific in tandem with initiatives such as-
- The Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI)
- To ensure Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR)
- India and some of the ASEAN countries are also members of the recently launched Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF).
- Checks Chinese Dominance: Maritime cooperation in terms of connectivity, safety and security has gained high attention in the backdrop of China's advancements in the South China Sea.
- India will gain better positioning against China's increasing dominating presence in the area.

