Nanomicelles: using nanoparticles for cancer treatment
Amulti-disciplinary, multi-institutional team has created a nanomicelle that can be used to deliver a drug named docetaxel, which is commonly used to treat various cancers including breast, colon and lung cancer.
Context
- Amulti-disciplinary, multi-institutional team has created a nanomicelle that can be used to deliver a drug named docetaxel, which is commonly used to treat various cancers including breast, colon and lung cancer.
What are nanomicelles?
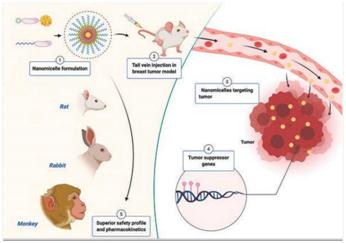
- Nanomicelles are extremely small structures and have been noted as an emerging platform in targeted therapy.
- Nanomicelles are globe-like structures with a hydrophilic outer shell and a hydrophobic interior.
- This dual property makes them a perfect carrier for delivering drug molecules.
- The nanomicelles are less than 100nm in size and are stable at room temperature.
How the drug delivery through nanomicelles works?
- The ideal goal for cancer therapy is destroying the cancer cells without harming healthy cells of the body.
- The currently used docetaxel is a highly hydrophobic drug, and is dissolved in a chemical mixture (polysorbate-80 and alcohol). This aggravates its toxic effects on liver, blood cells, and lungs.
- So nanomicelles acts as targeted drug delivery vehicles for docetaxel without these side effects
- Once injected intravenously these nanomicelles can easily escape the circulation and enter the solid tumours where the blood vessels are found to be leaky. These leaky blood vessels are absent in the healthy organs.