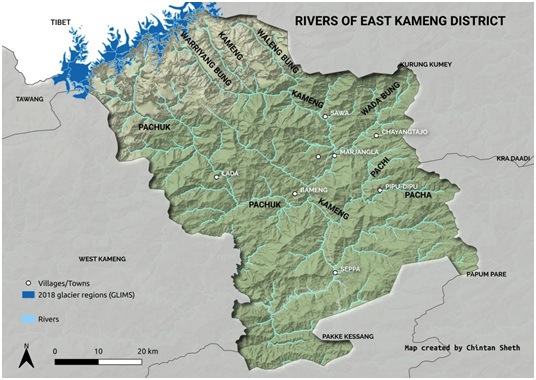
Mass Fish Death reported in Kameng River
Recent landslides caused by an earthquake of 3.4 magnitude close to the border with China has led to mass fish death in the Kameng river in Arunachal Pradesh.
Context
Recent landslides caused by an earthquake of 3.4 magnitude close to the border with China has led to mass fish death in the Kameng river in Arunachal Pradesh.
What led to the deaths?
- There is high content of Total Dissolved Substances (TDS) causing low visibility and breathing problems for aquatic species resulting in the death of thousands of fish.
- The landslides dumped several tonnes of mud and rocks into the river, substantially reducing the flow of water.
Effects of Low dissolved oxygen
- Low dissolved oxygen concentrations can arise through natural phenomena that include seasonality, changes in river flow, and both saline and thermal stratification of the water column.
- Low dissolved oxygen levels can also indicate an excessive demand on the oxygen in the system.
Kameng River
|