Edge Computing
Context
Siemens MindSphere and IBM forms partnership to target edge computing
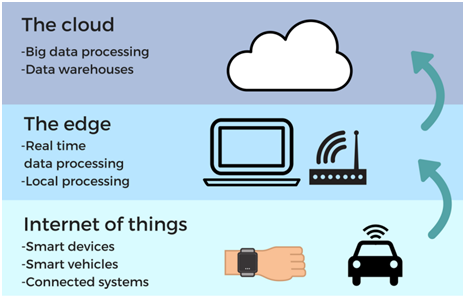
What is Edge Computing?
- Edge computing is computing that’s done at or near the source of the data, instead of relying on the cloud, one of a dozen data centers to do all the work.
- It is a part of a distributed computing topology in which information processing is located close to the edge – where things and people produce or consume that information.
- Applications-
- Autonomous and connected cars
- Smart cities
- Home automation
- Multiplayer gaming
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Privacy and security: Data may travel between different distributed nodes connected through the Internet, and thus requires special encryption mechanisms independent of the cloud. By keeping data at the edge it is possible to shift ownership of collected data from service providers to end-users.
- Speed: Edge computing brings analytical computational resources close to the end users and therefore helps to speed up the communication speed. A well designed edge platform would significantly outperform a traditional cloud-based system.
- Efficiency: Due to the proximity of the analytical resources to the end users, sophisticated analytical tools and Artificial Intelligence tools can run on the edge of the system. This placement at the edge helps to increase operational efficiency.

