Astrosat
Context
Astrosat, India’s first dedicated astronomy mission witnessed the birth of black holes for the five hundredth time.
What is a black hole?
- A black hole is a place in space where gravitational force is so high that even light cannot get out.
- High configuration space telescopes can help find black holes.
- Black holes in the modern sense were first predicted as a consequence of Albert Einstein’s general Theory of relativity in 1915.
- According to NASA, the gravity in black holes is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying.
- The gravity is so strong because the matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying.
- Because no light can get out, one can't see black holes. They are invisible.
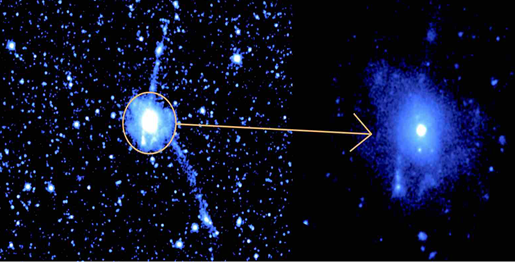
- Because no light can get out, one can't see black holes. They are invisible.
About AstroSat
- AstroSat is India’s first multi-wavelength space telescope, which has five telescopes seeing through different wavelengths simultaneously — visible, near UV, far UV, soft X-ray and hard X-ray.
- Onboard the AstroSat is a 38-cm wide UltraViolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT), which is capable of imaging in far and near-ultraviolet bands over a wide field of view.
- AstroSat was launched on 28 September 2015 by ISRO into a near-Earth equatorial orbit.
- It is a multi-institute collaborative project, involving IUCAA, ISRO, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (Mumbai), Indian Institute of Astrophysics (Bengaluru), and Physical Research Laboratory (Ahmedabad), among others.
- It has been studying Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRB).
What are Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRB)?
|

